(260) 356-2312
11 Jul Free Financial Health Resources for UB Pastors and Churches
The United Brethren denomination has been chosen to participate in a program which offers free financial health online courses and other resources. These are designed to help UB pastors, leaders, and congregations in the areas of personal finances and church generosity.
This is made possible because we are a member denomination of the National Association of Evangelicals. The Lilly Endowment provided a generous grant to the NAE to help member denominations improve the financial health of their pastors and churches.
The NAE set up a webpage for United Brethren which tells all about the program. The page includes a video by Bishop Todd Fetters.
An online course on Personal Finances begins in September, and a course for the broader church starts in January. Please register by August 31 to take advantage of these courses.
September: Personal Finances
This free online course begins in September, and includes six monthly sessions. It was specifically created for pastors and spouses, but any interested church staff, leaders, or members will also benefit from this training. The monthly sessions can be done at home on your own schedule.
Learn from Christian financial experts how to:
- Pay off debts.
- Increase savings.
- Track and decrease expenses.
- Prepare for retirement.
- Find affordable healthcare.
- Set financial goals.
- Increase your giving.
January: Church Generosity
This free online course will help you and your key leaders determine the best ways to improve the generosity and financial health of the people in your church.
The course was specifically created for a pastor and a group of lay leaders to do together. The six monthly sessions take 20-45 minutes to complete, depending on the amount of discussion.
Various resources—brochures, planning calendar, devotionals—will be available to those who register.
Visa eGift Cards
A limited number of $100 and $200 Visa eGift cards will be given to those who complete the courses.
Grants for Ministers
Grant funds will provide several kinds of financial assistance to pastors.
- Medical bill assistance grants of $2000 for unpaid medical bills of $2000 (up to 5 recipients).
- Student loan grants for church planters to help with school loan repayment.
- Retirement savings jump start grants of up to $1000.
- Emergency fund jump start grants of up to $500.
Create an account at NAEFinancialHealth.org/UB by August 31, 2018.
25 Jan Farewell and Best Wishes for Natania Kim
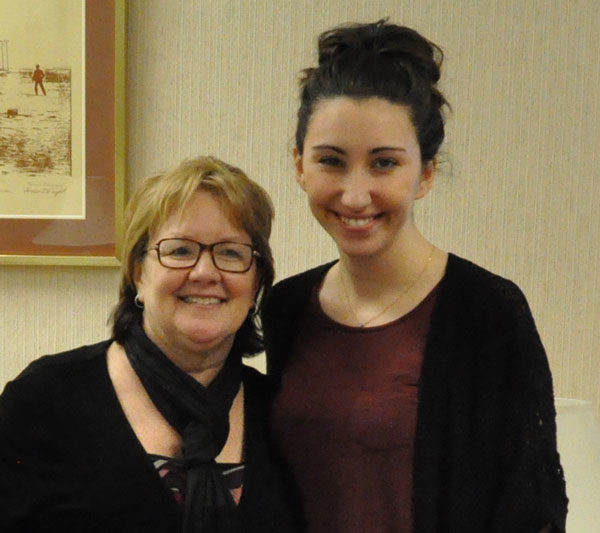
Cathy Reich (left) and Natania Kim.
On January 25, the United Brethren National Office held a goodbye celebration for Natania Kim, a Huntington University student who has worked part-time at the office for the past three years.
Natania began working at the UB National Office during the second semester of her freshman year. Classmate Taylor North, who had been doing some work at the National Office, mentioned that Cathy Reich, the administrative assistant to the bishop, was looking for some help. Natania ended up working a few hours a week with Cathy throughout her college years.
“Once in a while,” said Cathy, “someone comes across our path with a persona that is difficult to put into words. Natania is one of those. She is an exceptional person. She has a tender heart, a loving spirit, and excels at everything she touches. I’ve enjoyed the time we have worked together more than I could have imagined. She will be missed here at the office, but I’m so excited for her and Junoh’s future. And I pray that wherever she goes, whomever she touches, people will be impacted by her tender love for Jesus and people.”

Natania and Junoh.
Natania grew up Southern Baptist in Zion, Ill. She came to Huntington University for the Art program, but ended up switching to Social Work. She will graduate this spring. Graduating at the same time will be her husband, Junoh Kim. They were married in July 2017.
After graduating, Natania and Junoh will most likely move back to the Chicago/Wisconsin area. Junoh is considering an offer for an accounting position in Milwaukee. Natania anticipates possibly pursuing a masters in Social Work.
Natania will be missed. She enthusiastically tackled whatever job she was given, whether computer work or mailings or weeding around the building. And she got things done fast. It could be difficult keeping her busy. It was a joy having Natania in our midst for the past three years, and we wish her well.
31 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 31 (The Religious Telescope)
 The 1833 General Conference provided for establishing a United Brethren publishing house. It took shape in May 1834 in Circleville, Ohio, under the sponsorship of Scioto Conference. William Rinehart, a United Brethren minister in Virginia Conference, had been publishing a paper on his own press called The Mountain Messenger. Scioto asked Rhinehart to move to Circleville to become editor of a United Brethren publication, and they even bought out his little paper.
The 1833 General Conference provided for establishing a United Brethren publishing house. It took shape in May 1834 in Circleville, Ohio, under the sponsorship of Scioto Conference. William Rinehart, a United Brethren minister in Virginia Conference, had been publishing a paper on his own press called The Mountain Messenger. Scioto asked Rhinehart to move to Circleville to become editor of a United Brethren publication, and they even bought out his little paper.
On December 31, 1834, the first issue of The Religious Telescope was published. It was four pages long, 15-by-22 inches in size. It began as a bi-monthly publication, and started with about 1200 subscribers who paid $1.50 per year. We now had a denominational publication.
John Lawrence, who would become editor in 1852, wrote, “The paper was a very respectable sheet, well edited, yet not popular because of the extreme views which it advocated. It entered largely into the controversies of the times and earnestly and boldly, though not always prudently, marched in the front ranks of every reform.”
Most of the original United Brethren spoke German, and the German language predominated in United Brethren circles into the 1830s. Only two members of the 1821 General Conference were English. Others could preach in English, but German was their mother tongue. The 1821 Discipline was printed in both languages—German on the left, English on the right. It was an acknowledgement of what was coming.
The Germans, because of their unselfish missionary zeal, pretty much worked themselves out of a denomination. They so generously supported and promoted outreach to English people that by the 1830s, we had become (or were becoming) a predominantly English-speaking church. Most of the church’s expansion into the west–Ohio, Indiana, and elsewhere–occurred among English-speaking people.
From the beginning, The Religious Telescope was published in English. However, because of protests from some German-speaking folks that scant attention was being given to the German constituency, we launched a German-language periodical called Die Geschaftige Martha (The Busy Martha). It started in 1840, but ceased after two years. English, even in Pennsylvania, was clearly the future.
In 1885, seeing The Religious Telescope dominated by liberal voices, Milton Wright and others launched an alternative paper. They considered calling it The United Brethren, but instead settled on The Christian Conservator. When Wright’s followers split off, The Christian Conservator became the official publication of the “radical” United Brethren denomination. Its name was changed to The United Brethren in 1954. The magazine was discontinued in 1993.
The Religious Telescope continued until 1946, when the “liberal” UBs merged with the Evangelical Association, which had its own publication called The Evangelical Messenger. The new denomination, called the Evangelical United Brethren Church, merged the two periodicals under the very uncreative name The Telscope-Messenger.
30 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 30 (Bethel Mote)

Bethel Mote
Bethel Mote, one of the longest-serving UB missionaries at 22 years, passed away on December 30, 2000. She was 77 years old.
Bethel grew up on a farm near Lake Odessa, Mich., and attended the Pleasant Valley UB church. She spent six terms in Sierra Leone from 1951-1973. Initially, Bethel served as matron at the Minnie Mull Girls School, taking charge of about 100 girls ages 5-13 in a boarding home. Later, she transferred to Bumpe, where she became principal, teacher, and boarding home manager of Bumpe Girls’ School.
Bethel returned to the States in 1973, settling in Lake Odessa and attending her home church of Pleasant Valley. The cause of death was cirrhosis of the liver, which a doctor said probably resulted from malaria she contracted in Sierra Leone.
29 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 29 (Dr. M. I. Burkholder)
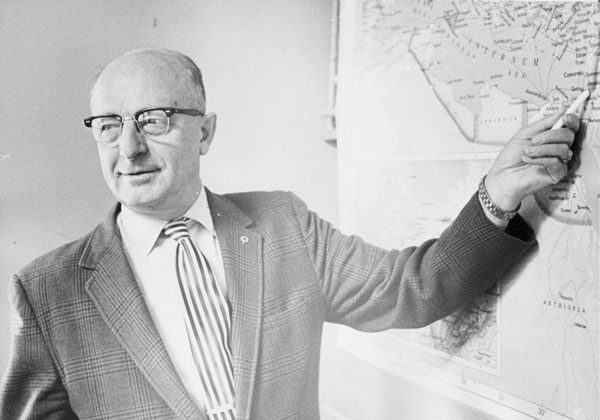
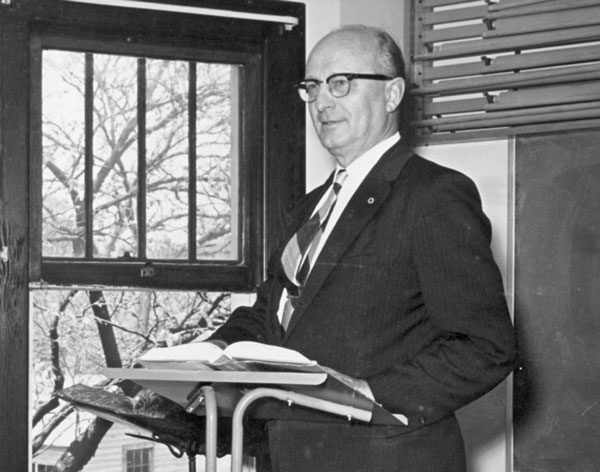


Dr. M. I. Burkholder in the classroom, teaching current and future United Brethren ministers.
Dr. M. I. Burkholder passed away on December 29, 1987. As dean of the Huntington College Seminary for 30 years, 1942-1972, he helped educate scores of United Brethren ministers, including future bishops.
Dr. Paul Fetters, one of his students, wrote in 1967, “M. I. Burkholder, Th. D., is a man qualified for the office of bishop, but has been needed to serve our church in our Huntington Theological Seminary….The men elected to the high office of bishop for the next several quadrenniums will reflect the influence of Dr. Burkholder.”
Burkholder grew up on a farm and attended a United Brethren church near Shippensburg, Pa. He was converted in 1917 through his pastor, future bishop Ezra M. Funk. He graduated from Huntington College in 1939, completed the Bachelor of Divinity in 1940, and two years later became dean of the HC Theological Seminary. Students not only sat under his teaching, but also under his preaching, since he pastored three different churches in the Huntington area: Union Church, an independent congregation outside of town (1944-1946); College Park Church (1946-1951); and what is now New Hope UB church (1951-1958).
In 1951, Burkholder became the first UB ordained minister to earn a doctorate — the Doctor of Theology from Northern Baptist Theological Seminary. Huntington College added an honorary doctorate in 1978. Dr. Burkholder retired in 1972, and Dr. Fetters took his place as dean of what became the Graduate School of Christian Ministries.
26 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 26 (Tsunami in India)
On December 26, 2004, an earthquake off the coast of Indonesia spawned a massive tsunami in the Indian Ocean. It killed a quarter-million people in Indonesia, Thailand, Malaysia, India, and elsewhere — and left countless others homeless and with destroyed livelihoods.
In India, the tsunami hit the state of Andhra Pradesh. Our workers there (we can’t name them on the internet), upon hearing horror stories from villages along the coast, spun into action to help people with medical care, food, clothing, shelter, etc. UB Global channeled contributions from people in North America to India.
On the Sunday after the tsunami, this couple visited seven churches and distributed clothes. In one small church, the pastor and members had been making their needs known to the Lord. When they showed up with clothes, it was a direct answer to their prayers.
In one village they found a group of fisherman who were all Christians. Many had lost their nets and had boats damaged. They were overjoyed that God answered their prayer for clothes and other help. One folks reported, “We saw many who were old and seemed to have lost all hope, and they were so delighted to receive some clothes for their use and have someone inquire of their welfare.”
A 16-year-old boy flagged down their car and begged them to come to his village, which had not yet received any help. They found about 40 families, most of them Christians. They distributed clothes and promised to return later. “We felt so satisfied to know that we had gone where no one had helped; it was really the Lord’s leading to take us there.”
About 5000 tsunami victims came to their city, either because their homes were destroyed or as a precaution against follow-up waves. Many stayed in nearby schools and colleges, including the United Brethren school they operated, where they received shelter and food.
At six schools, our couple gave away over 1000 bags containing plates, glasses, and a lunch box. In eight fishing villages, they went house-to-house distributing bags containing various items useful in the home — pots and pans, spoons, towels, saris, glasses, and steel storage containers. Since drinking water was hard to get and women needed to haul water long distances, they gave out steel water pots for carrying water. They wrote in the Missions Impact newsletter:
“They were so grateful to get these items. We personally handed these items to them in their homes, along with gospel tracts. We wish you could have seen the delight in their eyes when they received this bag full of things. These people live entirely on fishing. They take out heavy loans at a very high interest rate, usually from people who take the fish from the daily catch as payment on the loan. Fishermen seem to be in a cycle of perpetual loans and poverty. It was a ray of hope to see that they are sending their children to school to enable them to escape this cycle.”
In two villages, they saw uncompleted church buildings which, because of the tsunami, would probably be left unfinished. These were the only churches in those villages (along with a Hindu temple). “We helped make sure that these buildings were completed. When we delivered relief items in these villages, we took the pastor with us to encourage villagers to come to church and know more about the compassion and love of our Lord Jesus.”
In one village, they conducted evangelistic meetings for two nights. Each night 300-350 people attended, 70% of them Hindus. They were very receptive to the Gospel, and 37 persons raised their hands to make commitments to Christ. Those who could read and write handed in decision cards. Our couple followed up by introducing them to local churches.
In each village, Hindu leaders expressed their gratitude. They appreciated the work being done by Christians.
23 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 23 (Managua Earthquake)
A 6.3 magnitude earthquake shattered Managua, Nicaragua, on December 23, 1972, killing 10,000 people and leaving 300,000 homeless. Communication with the United Brethren pastors and people in Nicaragua was lost. Honduras Conference had begun ministry in Nicaragua during the mid-1960s, and we had several churches there.
On January 5, Honduras missionary Archie Cameron contacted the Missions department in Huntington, Ind., reporting that our workers in Nicaragua had escaped personal harm, but that they had relatives, friends, and neighbors who had lost a great deal. The Missions department issued an emergency appeal for relief money, and within a few months, nearly $20,000 had been raised.
Cameron and fellow UB missionary Gary Brooks arrived in Managua on March 19, 1973. As they approached the city center, they saw hundreds of refugee tents and lines of people waiting for food and medical attention. Damaged buildings stood everywhere, with people busily repairing cracks in walls.
Then they arrived at the center of Managua. Going past a barbed wire fence, they drove block after block without finding a single building still standing. There were thousands of fallen homes and stores, and not a living soul in sight. Brooks wrote:
“The overwhelming silence inside the fence prevails. One finds himself searching for signs of life, knowing there is none to be found. Over 7000 people died here–some immediately, and others after days of suffering. We could still smell the stench of rotting bodies under one fallen building. It is said that the wrecking crews find an average of 40 bodies per day….The residential areas of the city are slowly stirring back to life, but not the center of the city. The heart of Managua stopped beating that warm December morning nearly four months ago, and the city died. This week, I saw its tomb.”
Nicaraguan dictator Anastasio Somoza Debayle named himself head of the National Emergency Committee, personally directing the international relief efforts. He used the position to plunder most of the relief money and supplies, and gave reconstruction contracts to family and friends. Such reports prompted baseball star Roberto Clemente to organize and personally accompany relief flights into Nicaragua. The fourth flight crashed, killing Clemente and others aboard.
Outrage against the Somoza regime’s actions after the earthquake gave substantial support to the opposition Sandinista rebels, who overthrew Somoza in 1979.
22 Dec UB Offices Closed Next Week
The United Brethren National Office will be closed December 23 – January 1. The office will reopen on January 2.
19 Dec On This Day in UB History: December 19 (John McNamar)

The gravestone of Rev. John McNamar, the first English-speaking UB preacher.
John McNamar was married December 19, 1805, in Xenia, Ohio. We can assume they said their vows in English, because McNamar is heralded as the first English-speaking United Brethren minister. Says so on his gravestone. All of the founders and early ministers spoke German. But in the early 1800s, most of the church’s westward expansion occurred among English-speaking people, and McNamar was in the forefront.
McNamar was born in Virginia in 1779, of Scottish-Irish descent. It’s not know when exactly he moved to Ohio. However, in 1811 he became a schoolteacher in Germantown, Ohio, where future bishop Andrew Zeller lived. He became a Christian during an evangelistic meeting in Zeller’s barn, and Zeller shepherded im toward the ministry. In 1814 he became a minister in Miami Conference (the Miami Valley of southwestern Ohio) and was ordained in 1816.

John McNamar
John Lawrence wrote, “He devoted himself to the Master’s work with a singleness of aim, and resoluteness of purpose, which have seldom been equaled. He planted the larger part of the early English United Brethren churches in southwestern Ohio and southern Indiana.” He was also successful in recruiting new ministers. By 1820, another eight English-speaking ministers had joined Miami Conference and were doing their own part in spreading the Gospel.
McNamar is described as brave, unpretentious, practical. He spoke slowly and distinctly, and used a lot of humor. He zealously expounded on and defended the fundamental Christian doctrines, like the divinity of Christ, which he often preached to “immense congregations at camp-meetings.” He was a strong theologian and could wax eloquent. But, “His object was to save men; and he had the happy faculty of following up a clear exposition and masterly defense of some great truth with a heart-searching application.”
William Weekley wrote, “Mr. McNamar had the evangelistic spirit to an intense degree, and the spread of the Redeemer’s kingdom was to him paramount to all things else. He had the zeal of the early disciples, and, regardless of the cost to himself, went everywhere in his large frontier parish preaching the gospel of the kingdom. He was a man of superb courage. To him even roads and paths seemed useless. If his horse could not carry him, he led the horse, or, leaving him behind, went on foot. He frequently slept in the wilderness, but he was never lost. His long journeys were often made extremely difficult by untoward condition of the roads and by overflowing creeks and rivers.”
Despite having to travel long distances over rough terrain, he was known for punctuality. Fellow minister George Bonebrake testified, “When the time arrived for him to start to an appointment, he was off. He would wait for no one, and listened to no excuses. Rain, snow, mud, swollen streams, and floating causeways–any of these, of all of them combined, could not change his purpose. Nothing but a physical impossibility would detain him from an appointment.”
Weekley said multitudes of people flocked to hear McNamar preach. “He was unsurpassed in his qualities to capture new communities. There must have been peculiar power in his preaching and a peculiar adaptability to the hearts and to the spiritual needs of the people.”
By all accounts, McNamar was a gifted, natural leader. He became highly respect in the denomination and helped shape important legislation. He was elected bishop in 1833 to succeed Christian Newcomer (who had died during his final term in office), but he declined for unknown reasons. However, he seemed to prefer working in the trenches. Henry Spayth wrote, “J.C. McNamar, a true son of the gospel, determined to march in the front ranks of the ministerial army. He chose the frontier country for his field of gospel labor. To forego all sorts of comfort, to range the forest, to carry the gospel to the newly-arrived inhabitants, to seek the lost and scattered of Israel, was his employment, no matter how poor or destitute they or himself were.”
McNamar toiled faithfully for over 30 years. He passed away in 1846.


